Win More Deals. Onboard Faster.
Projetly is an AI-powered GTM execution platform unifying Digital Sales Rooms, Customer Onboarding, and Client Collaboration. It transforms closed deals into AI-assisted onboarding plans, auto-generates tasks, and delivers real-time insights.
Without shared visibility, buyers disengage, deals stall, and you lose control of the sales process.
Context Gets Lost in Handoff
Sales closes the deal, but onboarding starts from scratch. Customers get frustrated and time-to-value slows.
Tool silos, manual processes, and unclear ownership extend timelines and burn out your team.
You're guessing what to do next. No deal insights. No risk signals. No evidence-backed guidance.
AI Tracks Deal Engagement in Real Time
AI monitors buyer activity and meeting signals to detect disengagements. Keep deals from going dark.
AI Delivers Evidence-Backed Guidance
AI analyzes buyer activity and sentiment to detect risks and recommend next actions. Backed by real execution data.
AI Automation + Token Rewards

💎 Plus: Token rewards powered by smart contracts to align teams and customers. Learn More →
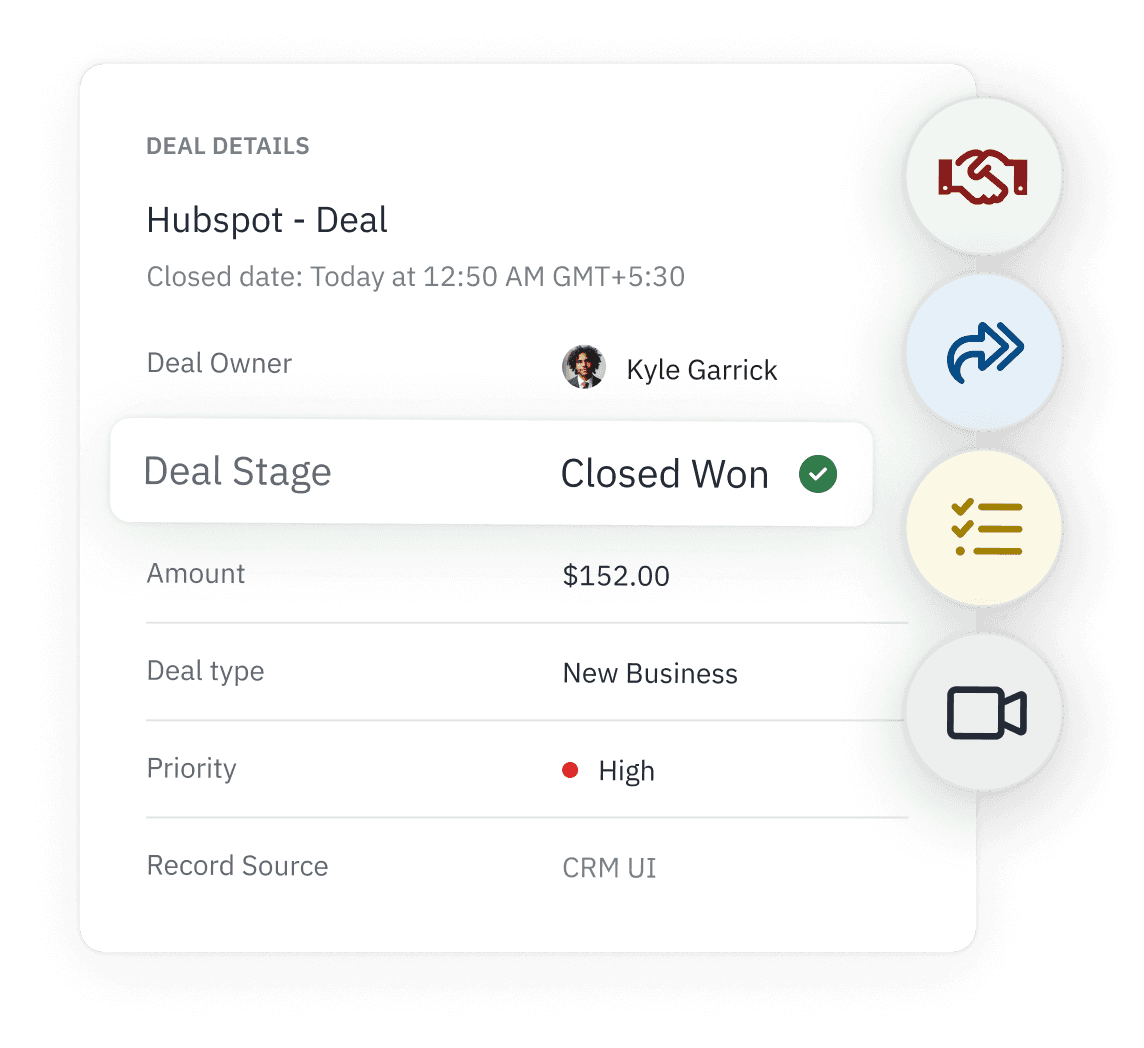
AI Transforms Deals Into Onboarding Plans
AI turns closed deals into structured onboarding workflows. No manual handoffs. No information lost.

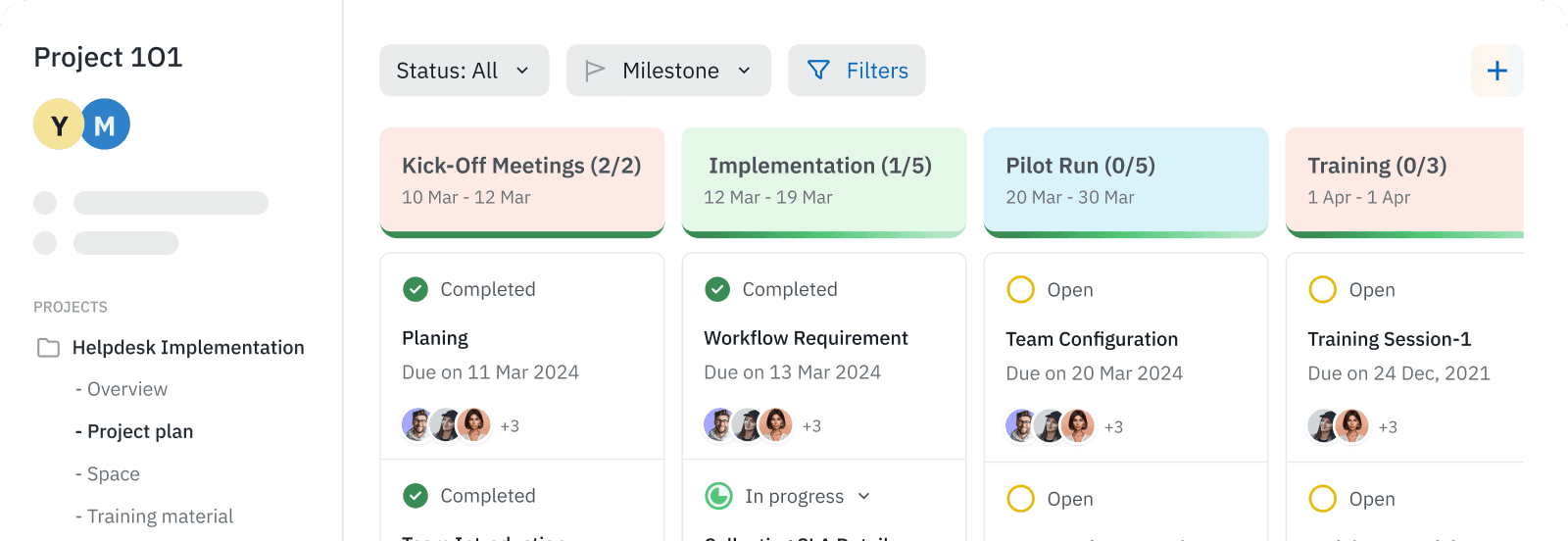
AI Automates Repetitive Work
AI automates meeting notes, tasks, events, and updates so your team can focus on execution.
One AI-powered workspace where sales, onboarding, and customers collaborate in real time with full visibility and zero information loss.

How Projetly Creates a Better Customer Experience
Why GTM Teams Choose Projetly
Without Projetly
40+ hours/month on manual deal tracking
Losing deals to competitors with no visibility
50% context loss in sales-to-onboarding handoff
30-60 day average onboarding timeline
With Projetly
5 hours/month (AI automates tracking)
20-30% increase in deal win rates
0% context loss (automated handoff)
15-30 day onboarding (AI workflows)